TMP42x HAL Based Library
The TMP421, TMP422, and TMP423 are remote temperature sensor monitors with a built-in local temperature sensor. The remote temperature sensor diode-connected transistors are typically low-cost, NPN- or PNP-type transistors or diodes that are an integral part of microcontrollers, microprocessors, or FPGAs. (Click for more info)
This library is a software library that works with the TMP42x remote and local temperature sensor. This library provides a convenient and efficient way to access the I2C interfaces of the chip, allowing developers to easily integrate this sensor into their systems.
The library is designed to be easy to use and provides a simple, intuitive API for accessing the I2C interfaces of the TMP42x. It includes a range of functions for performing common I2C operations, such as sending and receiving data, querying the status of the chip, reading the measured parameters, and configuring the TMP42x settings.
With this library, developers can quickly and easily integrate the TMP42x into their systems, enabling them to take full advantage of the chip's capabilities.

Key Features
- Easy-to-use API for accessing the I2C interfaces of the TMP42x
- Support for common I2C operations, such as sending and receiving data, querying the status of the chip, reading the measured parameters, and configuring the TMP42x settings
- Full feature library
Documentations
The full documents are available here
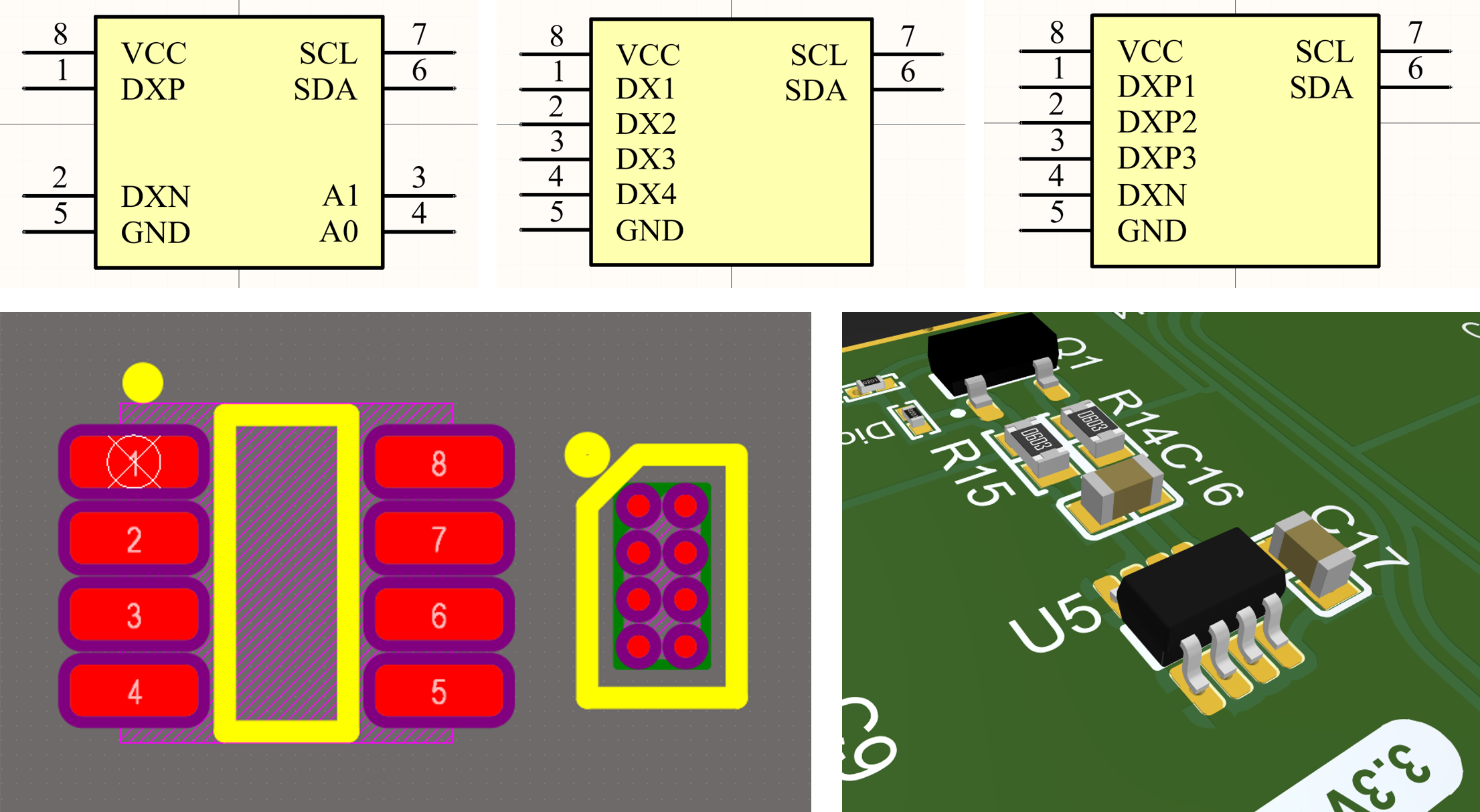
Schematic Symbol and Footprint
Footprint and schematic symbols are available in my Altium library.
Donate
Is it helpfull?
Getting Started
Quick Start
- Download the library source from the latest release
- Copy
TMP42x.candTMP42x.hfile to your project directory and add them to your IDE if necessary. - Inclued the library into your project:
- Create an object (instanse) from TMP42x struct with desired name. I named it tmp422 as an example:
- Initialize the chip: Each argument is described on the doc page.TMP42x_Status TMP42x_init(TMP42x *self, TMP42x_Type type, I2C_HandleTypeDef *hi2c, uint8_t I2C_ADDR, TMP42x_Shutdown shutdown, TMP42x_Range range, TMP42x_ConversionRate conversion_rate, float n_eff1, float n_eff2, float n_eff3)Initialize the TMP42x with the given config.Definition TMP42x.c:138
- Now you can call
TMP42x_getRemoteTempfunction to read the meassured data:double remote_temp1 = TMP42x_getRemoteTemp(&tmp422, 1);double remote_temp2 = TMP42x_getRemoteTemp(&tmp422, 2);double local_temp = TMP42x_getLocalTemp(&tmp422);double TMP42x_getLocalTemp(TMP42x *self)Reads the full (floating-point) local temperature from a specified channel.Definition TMP42x.c:262double TMP42x_getRemoteTemp(TMP42x *self, uint8_t channel_number)Reads the full (floating-point) remote temperature from a specified channel.Definition TMP42x.c:217
Here is the whole code:
If you want to use UART or virtual USB COM port on youe microcontroller, it is recommended to use this print function:
By applying the above trick, you can simply use this one to see the variables on the serial terminal:
Advanced Options
Getting the Integer Part of the Temperature
You can read the integer part of the temperature value by calling TMP42x_getRemoteTemp_Int and TMP42x_getLocalTemp_Int
Each function is described on the doc page.
One-Shot Trigger
Instead of continous conversion (run mode), you can read start a single conversion when the device is in shutdown mode by calling the TMP42x_oneShotStart function (see more)
Soft Reset
You can send a reset command to TMP42x chip by calling TMP42x_softwareReset function. (see more)
Getting Manufacturer and Device ID
If you want to get the manufacturer or device ID, you can use these functions:
For example:
